Rat TrkB / NTRK2 Protein (Fc Tag)
NTRK2, Trkb
- 100ug (NPP3093) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80243-R02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | NTRK2, Trkb |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant Rat NTRK2/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 639 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 71.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 120 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Cys 32 |
| SDS-PAGE | 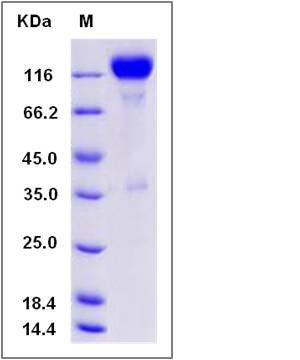 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the Rat NTRK2 (NP_036863) (Met1-His429) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Akt Pathway |Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | TrkB receptor also known as TrkB tyrosine kinase or BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor or neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type 2 (NTRK2) is a single transmembrane catalytic receptors with intracellular tyrosine kinase activity. TrkB/NTRK2 is a member of the neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) family. TrkB tyrosine kinase (TrkB) or NTRK2 is coupled to the Ras, Cdc42/Rac/RhoG, MAPK, PI3-K and PLCgamma signaling pathways. There are four members of the Trk family; TrkA, TrkB and TrkC and a related p75NTR receptor. Each family member binds different neurotrophins with varying affinities. TrkB/NTRK has highest affinity for brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and is involved in neuronal plasticity, longterm potentiation and apoptosis of CNS neurons. Other neurotrophins include nerve growth factor(NGF), neurotrophin-3 and neurotrophin-4. TrkB/NTRK is a membrane-bound receptor that, upon neurotrophin binding, phosphorylates itself and members of the MAPK pathway. Signalling through this kinase leads to cell differentiation. Mutations in TrkB/NTRK have been associated with obesity and mood disorders. |
| Reference |
