Rat VEGFC / VEGF-C Protein (aa 108-223, Fc Tag)
VEGFC
- 100ug (NPP1613) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P80103-R01H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rat |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | VEGFC |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant Rat VEGFC/Fc comprises 376 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 41.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 44 and 34 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu |
| SDS-PAGE | 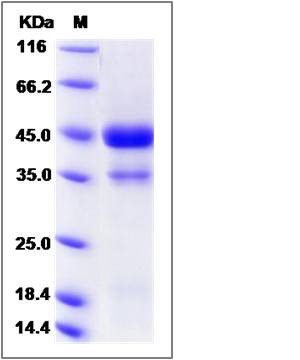 |
| Purity | > (73+25.1) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rat VEGFC (O35757) (Ala108-Arg223) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Immobilized mouse FLT4-His (P50584-M08H) at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind rat Fc-VEGFC, The EC50 of rat Fc-VEGFC is 0.41-0.95 μg/mL. 2. Measured in a cell proliferation assay using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). The ED50 for this effect is 20-100ng/mL. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) & Receptor |Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a member of the VEGF family. Upon biosynthesis, VEGF-C protein is secreted as a non-covalent momodimer in an anti-parellel fashion. VEGF-C protein is a dimeric glycoprotein, as a ligand for two receptors, VEGFR-3 (Flt4), and VEGFR-2. VEGF-C may function in angiogenesis of the venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis. VEGF-C protein is over-expressed in various human cancers including breast cancer and prostate cancer. VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 axis, through different signaling pathways, plays a critical role in cancer progression by regulating different cellular functions, such as invasion, proliferation, and resistance to chemotherapy. Thus, targeting the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 axis may be therapeutically significant for certain types of tumors. |
| Reference |
