Rhesus ACVR1B / ALK-4 Protein (Fc Tag)
ACVR1B
- 100ug (NPP1038) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90066-C02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rhesus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ACVR1B |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rhesus ACVR1B comprises 341 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 38.2 KDa. |
| predicted N | Arg 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 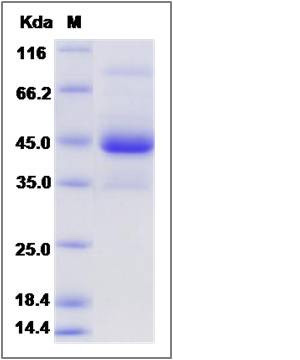 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus ACVR1B (NP_001252559.1) (Met1-Glu126) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Oncoprotein |Growth Factor & Receptor |Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-beta) Superfamily |TGF-beta Superfamily Receptors | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | ALK-4 (Activin Receptor-Like Kinase 4) or ACVR1B (Activin A Receptor, type 1B), belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, TKL Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and TGFB receptor subfamily. ALK-4/ACVR1B acts as a transducer of activin or activin like ligands signals. Activin binds to either ACVR2A or ACVR2B and then forms a complex with ACVR1B. The known type II activin receptors include ActRII and ActRIIB, while the main type I activin receptor in mammalian cells is ALK-4 (ActRIB). In the presence of activin, type II and type I receptors form complexes whereby the type II receptors activate ALK-4 through phosphorylation. The activated ALK-4, in turn, transduces signals downstream by phosphorylation of its effectors, such as Smads, to regulate gene expression and affect cellular phenotype. ALK-4/ACVR1B is an important regulator of vertebrate development, with roles in mesoderm induction, primitive streak formation, gastrulation, dorsoanterior patterning, and left-right axis determination. |
| Reference |
