Rhesus EphA4 Protein (His Tag)
EPHA4
- 100ug (NPP2923) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90039-C08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rhesus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | EPHA4 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rhesus EPHA4 comprises 539 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 59.8 KDa. |
| predicted N | Val 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 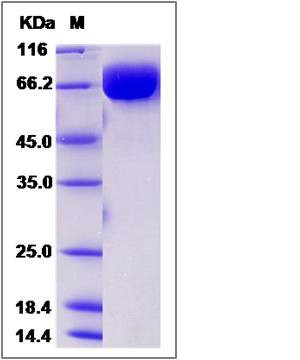 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus EPHA4 (NP_001247799.1) (Met1-Thr547) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Rhesus EPHA4-His at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind mouse EFNA5-Fc (P50597-M02H), The EC50 of mouse EFNA5-Fc (P50597-M02H) is 28.2-65.8 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | EPH receptor A4 (ephrin type-A receptor 4), also known as EphA4, belongs to the ephrin receptor subfamily of the protein-tyrosine kinase family which 16 known receptors (14 found in mammals) are involved: EPHA1, EPHA2, EPHA3, EPHA4, EPHA5, EPHA6, EPHA7, EPHA8, EPHA9, EPHA10, EPHB1, EPHB2, EPHB3, EPHB4, EPHB5, EPHB6. The Eph family of receptor tyrosine kinases (comprising EphA and EphB receptors) has been implicated in synapse formation and the regulation of synaptic function and plasticity6. EphA4 is enriched on dendritic spines of pyramidal neurons in the adult mouse hippocampus, and ephrin-A3 is localized on astrocytic processes that envelop spines. Eph receptor−mediated signaling, which is triggered by ephrins7, probably modifies the properties of synapses during synaptic activation and remodeling. Ephrin receptors are components of cell signalling pathways involved in animal growth and development, forming the largest sub-family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). The extracellular domain of an EphA4 interacts with ephrin ligands, which may be tethered to neighbouring cells. Ligand-mediated activation of Ephs induce various important downstream effects and Eph receptors have been studied for their potential roles in the development of cancer. |
| Reference |
