Rhesus KIM-1 / TIM1 / HACVR1 Protein (His Tag)
HAVCR1
- 100ug (NPP1630) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90006-C08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rhesus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | HAVCR1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rhesus HAVCR1 consists of 127 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 14 kDa. |
| predicted N | Asp 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 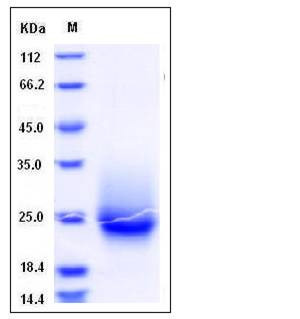 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus HAVCR1 (BAJ61041.1) N-terminal segment (Met 1-Val 135) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |Costimulation & Costimulatory Molecule |Other Costimulatory Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Human HAV cellular receptor 1 (HAVCR1), also known as Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) and T cell immunoglobulinmucin 1 (TIM-1), is a type â… integral membrane glycoprotein. KIM-1 protein is widely expressed with highest levels in kidney and testis. It has been shown to play a major role as a human susceptibility gene for asthma, allergy and autoimmunity. IgA1lambda is a specific ligand of KIM-1 protein and that their association has a synergistic effect in virus-receptor interactions. KIM-1 involves in the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury. It had been confirmed that KIM-1 is a human urinary renal dysfunction biomarker. Moreover, KIM-1 protein is a novel regulatory molecule of flow-induced calcium signaling. |
| Reference |
