Rhesus Layilin / LAYN Protein (Fc Tag)
LAYN
- 100ug (NPP2937) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90160-C02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rhesus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | LAYN |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant Rhesus LAYN is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 440 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 49.8 KDa.The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 58 KDa respectively in SDS-PAGE. |
| predicted N | Ala 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 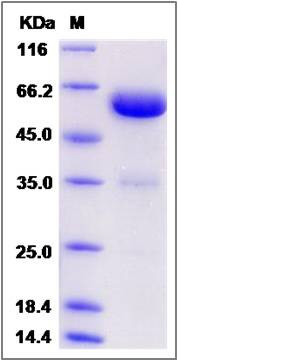 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus LAYN (XP_001105766.1) (Met1-Glu220) was expressed with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Invasion microenvironment |Adhesion molecule |Cell adhesion |Lectin |C-tyep lectin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Layilin, a recently characterized as a 55 kDa transmembrane protein with homology to C-type lectins, is present in numerous cell lines and tissue extracts. As one of the adaptor proteins, talin mediates the interactions between the actin filaments and the cell membrane by binding to integral membrane proteins and to the cytoskeleton. Layilin is a newly identified membrane-binding site for talin in peripheral ruffles of spreading cells, a ten-amino acid motif in the layilin cytoplasmic domain is sufficient for talin binding, and its adjacent LH2-LH3 tandem arrays in the cytoplasmic domain provide docking sites for talin. Furthermore, talin binds layilin, PIPK1gamma and integrins in similar although subtly different ways. Layilin binds specifically to hyaluronan (HA) through its extracellular domain, a ubiquitous extracellular matrix component in most animal tissues and body fluids, but not to other tested glycosaminoglycans. The research suggests that layilin may mediate signals from extracellular matrix to the cell cytoskeleton via interaction with different intracellular binding partners and thereby be involved in the modulation of cortical structures in the cell. All the above actions reveal an interesting parallel between layilin and the known HA receptor CD44. In addition, merlin and radixin have been identified as different intracellular binding partners of layilin. Accordingly, it has been suggested that layilin plays roles in a variety of cellular processes, including cell shape, adhesion, motility, and homeostasis, as well as signal transduction. In addition, layilin might play an important role in the process of invasion and lymphatic metastasis of lung carcinoma. |
| Reference |
