Rhesus SFTPD / SP-D / SFTP4 Protein (His Tag)
SFTPD
- 100ug (NPP2950) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90003-C08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rhesus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | SFTPD |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant rhesus SFTPD consists of 365 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 36.8 kDa. |
| predicted N | Asp 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 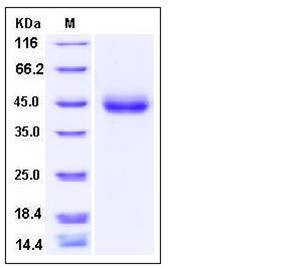 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus SFTPD (NP_001035283.1) (Met 1-Phe 375) precursor was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolism processes |Apoptosis | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Surfactant pulmonary-associated protein D, also known as SFTPD and SP-D, is a member of the collectin family of C-type lectins that is synthesized in many tissues including respiratory epithelial cells in the lung, and contains one C-type lectin domain and one collagen-like domain. The polymorphic variation in the N-terminal domain of the SP-D molecule influences oligomerization, function, and the concentration of the molecule in serum. SFTPD is produced primarily by alveolar type II cells and nonciliated bronchiolar cells in the lung and is constitutively secreted into the alveoli where it influences surfactant homeostasis, effector cell functions, and host defense. It is upregulated in a variety of inflammatory and infectious conditions including Pneumocystis pneumonia and asthma. SFTPD is humoral molecules of the innate immune system, and is considered a functional candidate in chronic periodontitis. Besides it is involved in the development of acute and chronic inflammation of the lung. Several human lung diseases are characterized by decreased levels of bronchoalveolar SFTPD. Thus, recombinant SFTPD has been proposed as a therapeutical option for cystic fibrosis, neonatal lung disease and smoking-induced emphysema. Furthermore, SFTPD serum levels can be used as disease activity markers for interstitial lung diseases. |
| Reference |
