Rhesus TRAIL R4 / CD264 / TNFRSF10D Protein (His Tag)
TNFRSF10D
- 100ug (NPP2953) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P90100-C08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Rhesus |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | TNFRSF10D |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant Rhesus TNFRSF10D comprises 162 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 17.3 KDa. |
| predicted N | Ala 56 |
| SDS-PAGE | 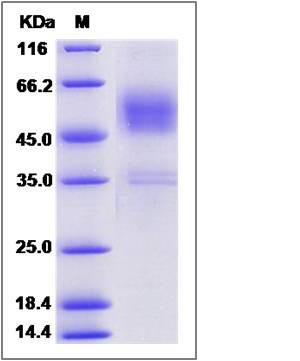 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the rhesus TNFRSF10D (XP_001107922.1) (Met1-Leu206) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) & Receptor |TNF Receptor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10D (TNFRSF10D), also known as TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 4 (TRAIL R4), CD264, and Decoy receptor 2, is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor contains an extracellular TRAIL-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and a truncated cytoplamic death domain. This receptor does not induce apoptosis, and has been shown to play an inhibitory role in TRAIL-induced cell apoptosis. TRAIL R4/CD264/TNFRSF10D is widely expressed, in particular in fetal kidney, lung and liver, and in adult testis and liver. TRAIL R4/CD264/TNFRSF10D is also expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes, colon and small intestine, ovary, prostate, thymus, spleen, pancreas, kidney, lung, placenta and heart. The signaling capacity of TRAIL R4 is similar to that of TRAIL R1 and TRAIL R2 with respect to NF-κB activation, but differs in its inability to induce apoptosis. TRAIL R4 retains a C-terminal element containing one third of a consensus death domain motif. Transient overexpression of TRAIL R4 in cells normally sensitive to TRAIL-mediated killing confers complete protection, suggesting that one function of TRAIL R4 may be inhibition of TRAIL cytotoxicity. |
| Reference |
