Schistosoma japonicumGlutathione S-transferase / GST Protein
GST
- 100ug (NPP2817) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11213-HNAB |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Schistosoma japonicum |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | GST |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant Glutathione S-transferase (GST) consists of 229 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 26.9 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of GST is approximately 28 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 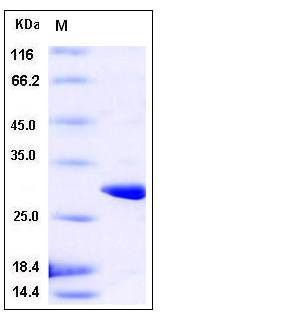 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the Glutathione S-transferase (P08515) (Met 1-Lys 218), with additional 11 amino acids at the C-terminus, was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Post embryonic development |Cellular Senescence & Aging |Oxidative Stress Enzymes |Antioxidant Enzymes |Glutathione S-transferase | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 2mM GSH, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Genetic engineers have used glutathione S-transferase to create the GST gene fusion system. This system is used to purify and detect proteins of interest. In a GST gene fusion system, the GST sequence is incorporated into an expression vector alongside the gene sequence encoding the protein of interest. Induction of protein expression from the vector's promoter results in expression of a fusion protein: the protein of interest fused to the GST protein. This GST-fusion protein can then be purified from cells via its high affinity for glutathione. GST is commonly used to create fusion proteins. The tag has the size of 220 amino acids (roughly 26 KDa), which, compared to other tags like the myc- or the FLAG-tag, is quite big. However, many commercially-available sources of GST-tagged plasmids include a thrombin domain for cleavage of the GST tag during protein purification. |
| Reference |
|
